(230215-bioRxiv) A Single-cell Perturbation Landscape of Colonic Stem Cell Polarisation - P1
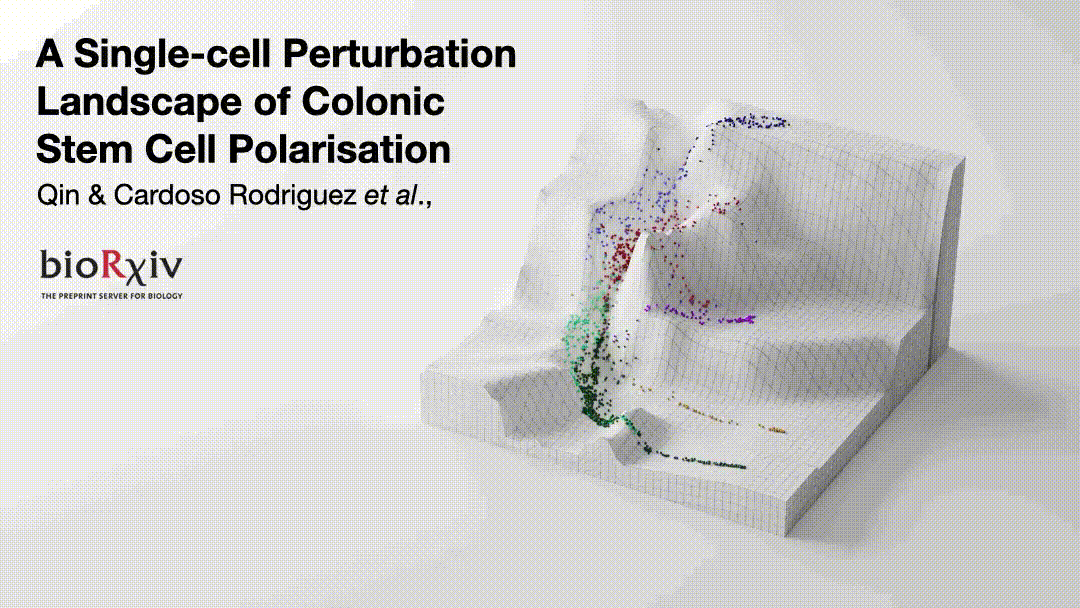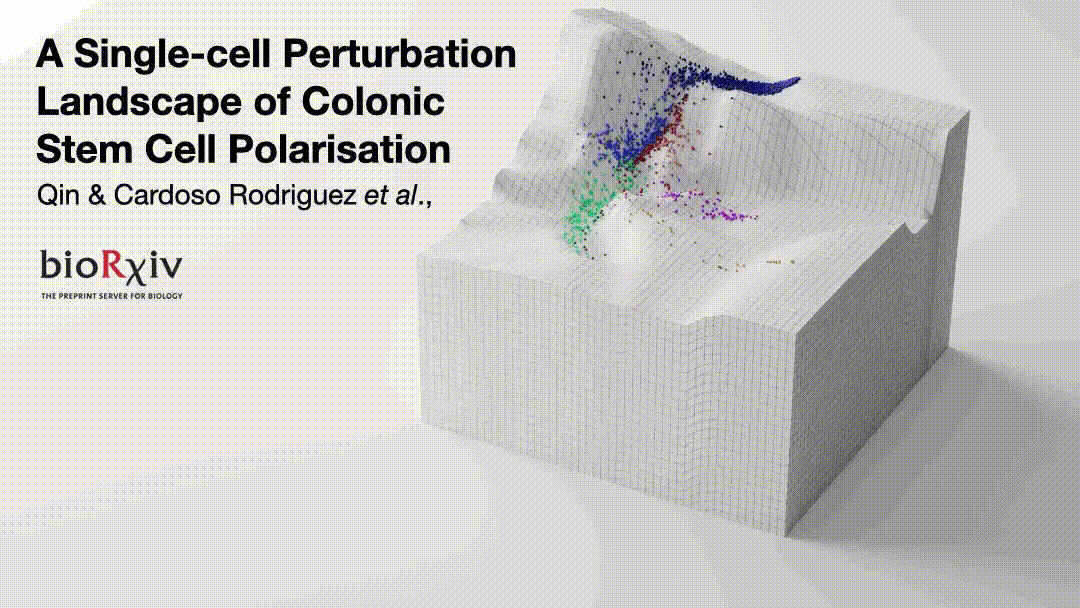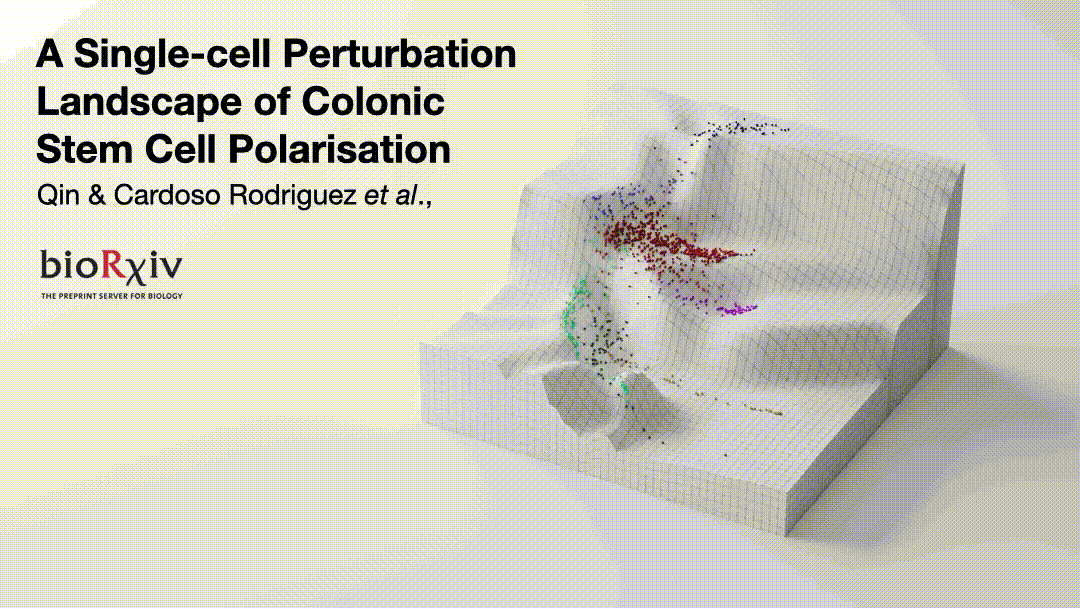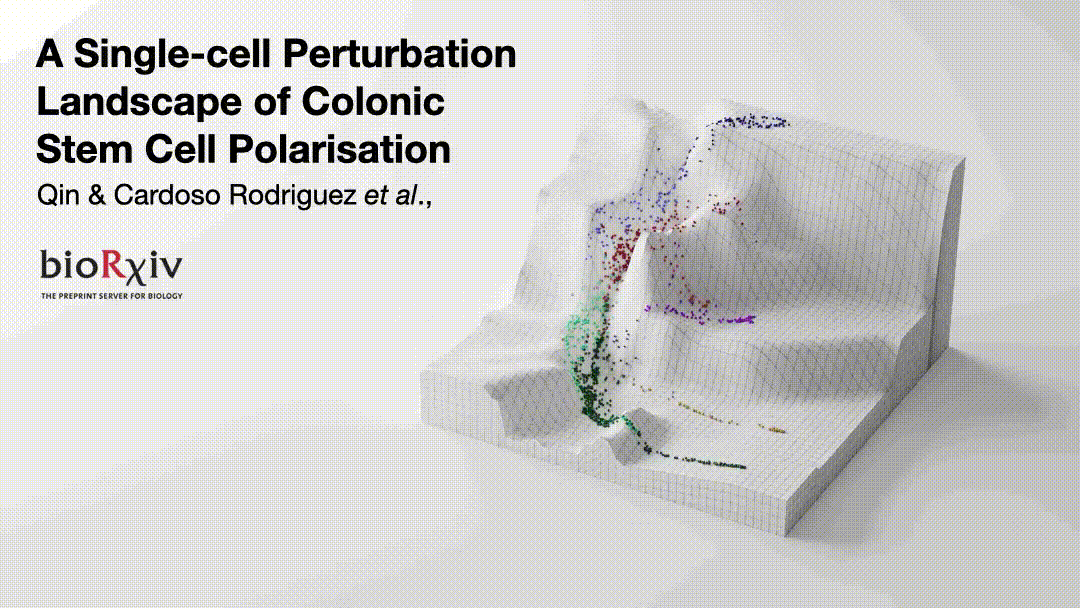
Cancer cells are regulated by oncogenic mutations and microenvironmental signals, yet these processes are often studied separately😕. To functionally map how cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic cues co-regulate cell-fate in colorectal cancer (CRC), we performed a systematic single-cell analysis of 1,071 colonic organoid cultures regulated by…
A Single-cell Perturbation Landscape of Colonic Stem Cell Polarisation
Qin et.al | bioRxiv | 2023.02.15.528008 | doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.15.528008
Author
Leader: Christopher J. Tape | UCL Cancer Institute
Focus on: How the different cell types in cancer communicate with one another to drive tumours
Work with: Organoid | scRNA-Seq | sc-MS
Website: The Cell Communication Lab: http://tape-lab.com/
Background
Intestinal cell type:
Ref
- intestinal stem cells and epithelium cells:
2021, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol
2019, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol
2010, Transl Res
2021, Cell Regen - intestinal mesenchymal cells:
2020, Nat Cell Biol
2020, Immunology
2022, Int J Mol Sci - intestinal immune cells:
2014, Nat Rev Immunol - intestinal neural cell:
2021, Front Physiol
2022, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol - intestinal single cell atlas:
2021, Nature
2021, Cell
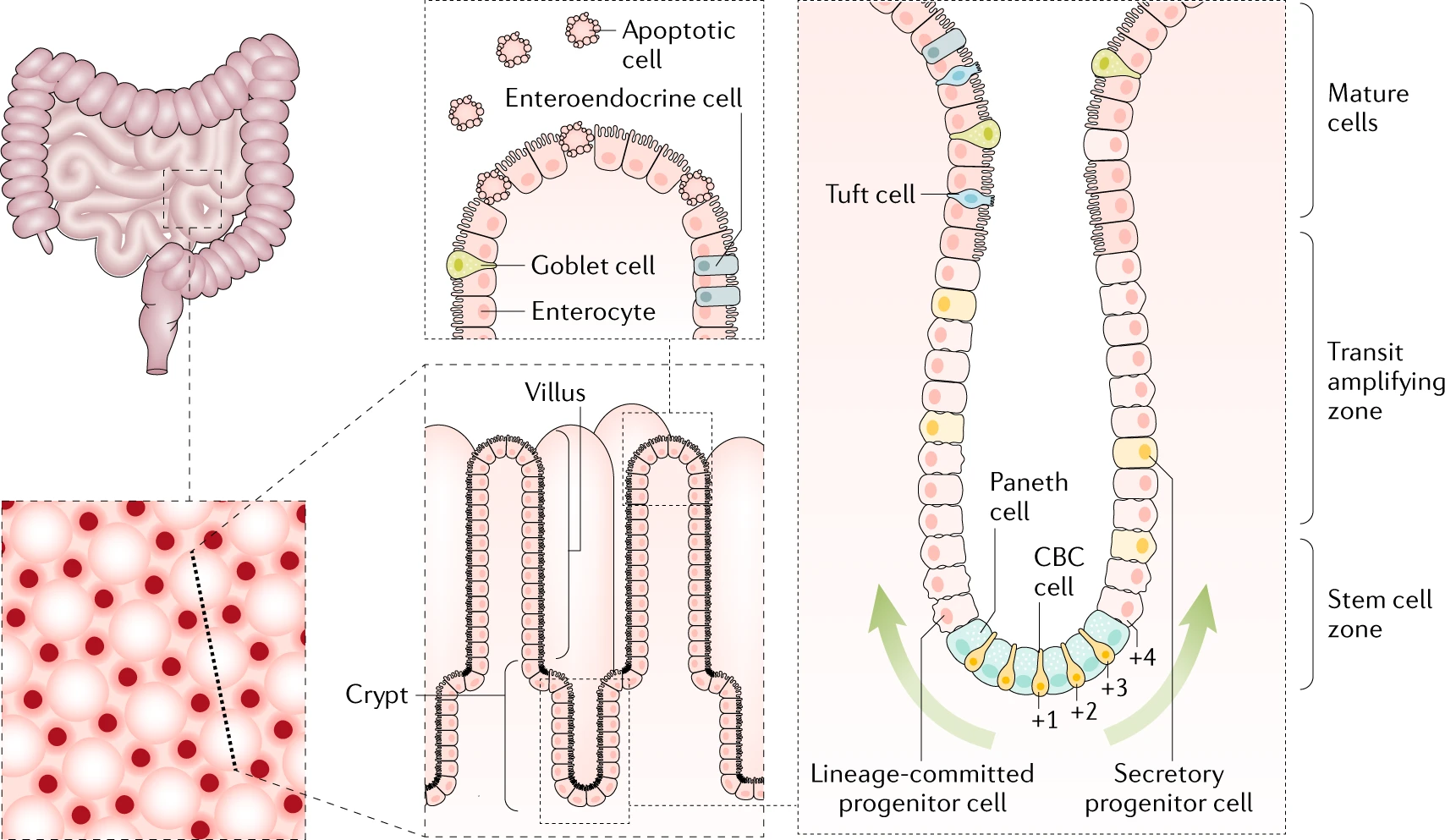
1. Intestinal stem cell (ISC):
- i.
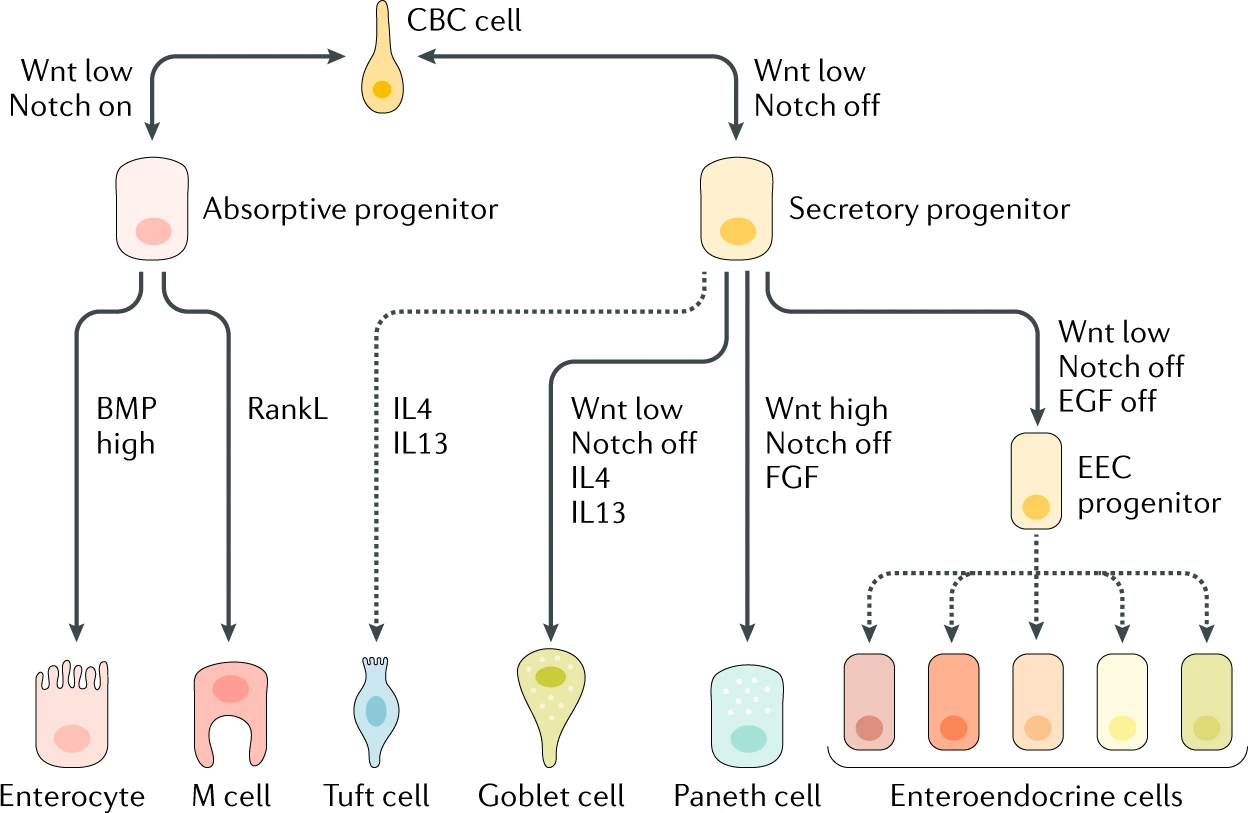
Crypt base columnar (CBC) cells: canonical/traditional/rapidly-cycling stem cell | generation of multiple lineages and long-term self-renewal | bottom of the crypt; interspersed between Paneth cells | LGR5+ OLFM4+ - ii.
+4 cells/Label-retaining cells (LRC): reserved/precursor/quiescent stem cell population 2013, Nature | +4 means located at the ~+4 from the crypt base;label-retaining means take advantage of these cells slow-cycling characteristic to take LRC approach (e.g. EdU labeling), a lineage tracing method, and LRCs are cells that retain a DNA synthesis label after a prolonged chase period | committed to mature into Paneth cells and EECs, but retain the ability to reacquire stem-cell function. At homeostatic/normal intestinal tissue they do not contribute cell turnover but can repopulate the crypt upon damage.
2. progenitor cells:
also named as transit-amplifying cells(TACs) (not accurate) | more specific than stem cells and can only be pushed to differentiate into its “target” cell type.
Adult stem cells usually reside in a specialized niche microenvironment (niche cells and the niche signals they produce), which provides necessary extracellular signals and substances to promote the long-term maintenance and self-renewal of stem cells
The epithelium and mesenchyme cooperate to generate the complex dynamic observed in intestinal crypts. Together they provide the key signals that regulate intestinal fate determination:
WNT,Notch,EGFandBMPsignalling
3. epithelium cell:
epithelium cell (especially Paneth cell) constitute the epithelial niche
Ref:
2022, Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol
2017, Nature
- i. Secretory lineage
- (1) Paneth cells:
- (2) Goblet cells
- (3) Enteroendocrine cells (EEC)
- (4) Tuft cells
- ii. Absorptive lineage
- (1) Enterocytes
- (2) M cells
here is epithelium cell specification:
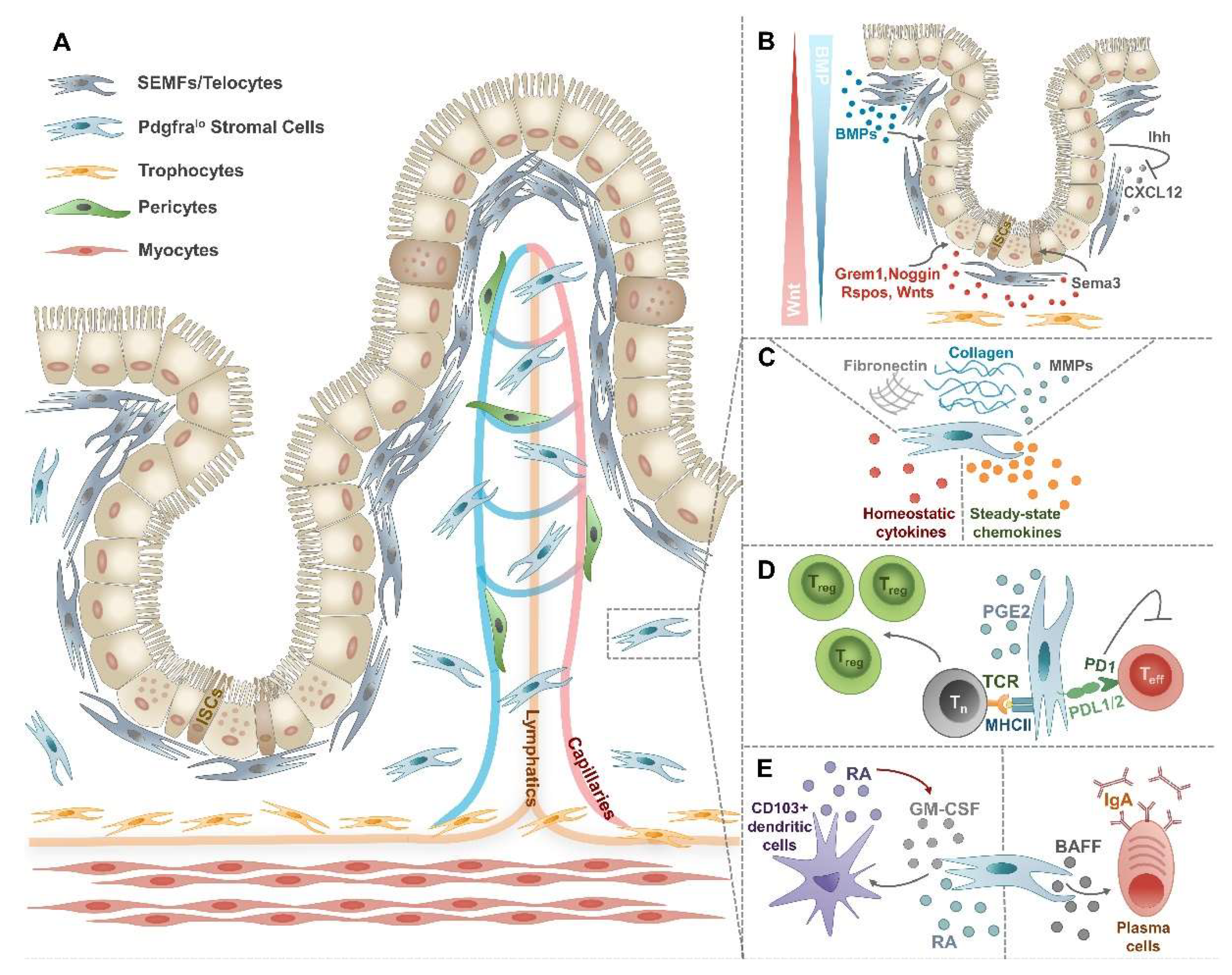
4. Intestinal mesenchymal (stromal) cell (IMC):
- Naming ambiguity: mesenchymal cell (MC) or stromal cell | mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) or mesenchymal stromal cell😤
- cancer-associated transdifferentiation: transdifferentiation of epithelial cells to mesenchymal cells (EMT); transdifferentiation of endothelial to mesenchymal cells (EndMT); transdifferentiation of mesothelial cells to mesenchymal cells (MMT)
- Most of IMC originates from the mesoderm and differentiates from mesenchymal stem cells, locate on subepithelial compartment, constitute the mesenchymal niche.
NOTE:for CRC IMC, here is a review:2017, Gastroenterology - subtypes:
pericyte; myofibroblasts (telocytes); fibroblast; xxx fibroblast…; myocytes (smooth muscle cells / muscularis).. (Foxl1+ MCs; Gli1+ MCs…)WarningHere is an unclear part, most people think
mesenchymal cellrepresent anon-hematopoietic, non-epithelial, and non-endothelial stromal compartments of connective tissues. They include highly diverse populations of fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, pericytes, smooth muscle cells, and mesenchymal progenitor cells, but Mesothelial cells is what?
A reasonable classification:
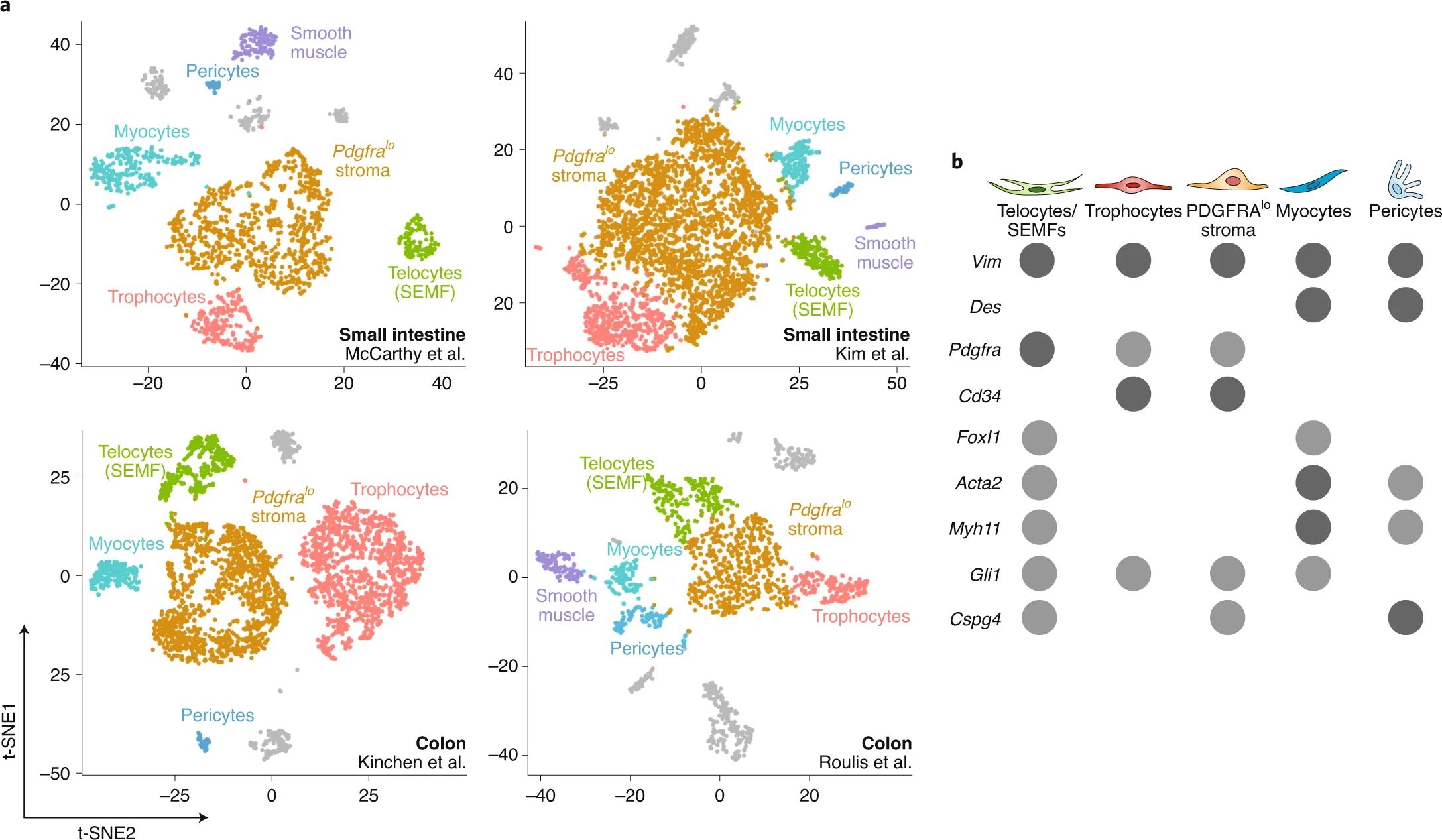
mesenchymal cells
5. Other cell types:
- i. Immune cells: ..
- ii. Endothelial cells:
- iii. Mesothelial cells: some papers seem classify mesothelial cells as mesenchymal (stromal) cell..?😤
- iv. intestinal neural cells: intestinal has its typical nervous system called intrinsic enteric nervous system (ENS): neuron and enteric glial cells (EGC)…
…
 Gaux Wang
Gaux Wang